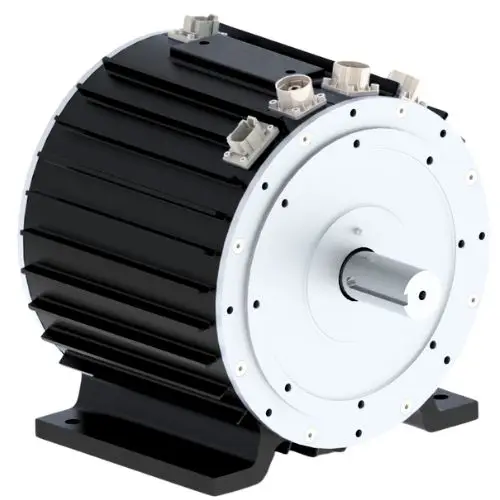

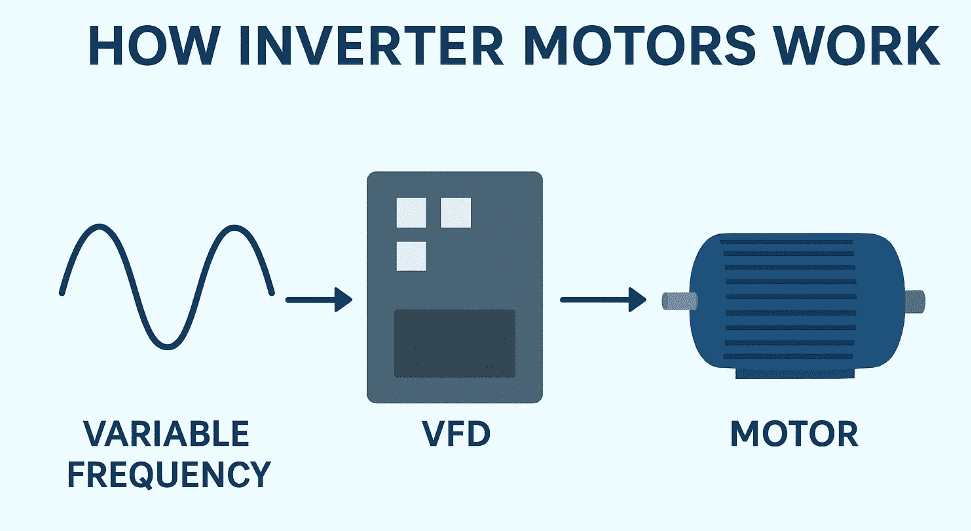
An inverter motor, also known as a variable-frequency drive (VFD) motor, is a modern electric machine designed to operate with a power electronic controller that regulates the motor’s speed and torque. Unlike traditional fixed-speed motors that are tied to the line frequency, an inverter motor adjusts its speed according to demand by varying the supply frequency and voltage. This ability to match performance with real-time application requirements makes the inverter motor highly energy efficient, durable, and versatile.
Today, inverter motors are widely used in various sectors, including electric and hybrid vehicles, material-handling systems, industrial automation, HVAC, and defence equipment. By enabling smooth control of acceleration, torque, and speed, these motors have transformed the way industries manage energy consumption and machine performance.
VFD Motor Offerings
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Model No. | Continuous Rating Power (kW) | Continuous Rating Torque (Nm) | Power (kW) at 60 Minutes | Torque (Nm) at 60 Minutes | Power (kW) at 15 Minutes | Torque (Nm) at 15 Minutes | Rated Speed (RPM) | Cooling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:47 AM | 255-AZZS565-002 | 1.0 | 91.4 | 1.1 | 113.5 | 1.4 | 176.2 | 100 | Natural |
| 2 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:47 AM | 255-AZZS565-006 | 3.7 | 46.7 | 4.7 | 58.2 | 7.5 | 92.5 | 750 | Natural |
| 3 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:47 AM | 255-AZZS565-012 | 7.5 | 46.7 | 10.2 | 57.6 | 14.8 | 92.5 | 1,500 | Natural |
| 4 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:48 AM | 255-AZZS565-014 | 8.5 | 47.6 | 11.8 | 59.3 | 18.7 | 94.2 | 1,800 | Natural |
| 5 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:48 AM | 255-AZZS565-016 | 10.0 | 46.6 | 12.8 | 58.2 | 20.0 | 92.3 | 2,000 | Natural |
| 6 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:48 AM | 255-AZZS565-024 | 15.0 | 46.7 | 20.6 | 58.1 | 32.8 | 92.5 | 3,000 | Natural |
| 7 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:51 AM | 360-AEZS400-065 | 27.0 | 317.6 | 33.5 | 395.7 | 52.6 | 621.0 | 800 | Natural |
| 8 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:51 AM | 360-AEZS565-065 | 35.0 | 317.4 | 53.7 | 395.5 | 76.0 | 621.0 | 1,000 | Natural |
| 9 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:52 AM | 360-AZZS400-040 | 17.3 | 217.0 | 27.0 | 270.3 | 40.0 | 424.0 | 760 | Natural |
| 10 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:52 AM | 360-AZZS400-050 | 20.0 | 81.4 | 28.2 | 270.3 | 44.3 | 424.0 | 900 | Natural |
| 11 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:52 AM | 360-AZZS565-014 | 8.8 | 213.0 | 11.0 | 265.0 | 17.2 | 416.0 | 400 | Natural |
| 12 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:53 AM | 360-AZZS565-040 | 20.0 | 217.0 | 30.5 | 270.0 | 48.0 | 424.0 | 900 | Natural |
| 13 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:53 AM | 360-AZZS565-050 | 28.0 | 217.0 | 39.5 | 270.3 | 55.8 | 424.0 | 1,200 | Natural |
| 14 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:54 AM | 360-BEZS565-030 | 18.0 | 570.0 | 23.3 | 708.8 | 27.8 | 1,109.2 | 300 | Natural |
| 15 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:54 AM | 360-CCC565S-022 | 13.5 | 716.7 | 16.8 | 891.6 | 26.3 | 1,398.6 | 180 | Natural |
| 16 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:50 AM | 360-CZZS565-020 | 12.3 | 651.9 | 15.3 | 811.0 | 24.0 | 1,272.0 | 180 | Natural |
| 17 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:50 AM | 360-CZZS565-022 | 14.0 | 645.5 | 17.4 | 803.3 | 24.2 | 1,260.0 | 200 | Natural |
| 18 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:50 AM | 360-CZZS565-024 | 14.7 | 626.4 | 18.3 | 779.6 | 28.8 | 1,224.2 | 220 | Natural |
| 19 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:55 AM | 360-DZZS565-030 | 18.0 | 912.0 | 23.5 | 1,134.0 | 32.7 | 1,774.8 | 190 | Natural |
| 20 | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:40 AM | Harshit | 16/04/2025 11:55 AM | 360-GZS565-002 | 1.0 | 152.0 | 1.2 | 189.2 | 1.6 | 297.0 | 60 | Natural |
| 21 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:36 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:36 AM | 360-GZS565-012 | 7.0 | 146.0 | 9.4 | 181.9 | 14.8 | 285.6 | 450 | Natural |
| 22 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:37 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:37 AM | 360-GZS565-014 | 8.5 | 149.0 | 11.0 | 185.6 | 17.2 | 291.2 | 550 | Natural |
| 23 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:38 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:38 AM | 360-GZS565-020 | 11.0 | 152.0 | 15.6 | 189.2 | 24.6 | 296.6 | 700 | Natural |
| 24 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:40 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:40 AM | 255-HZS565-012 | 7.5 | 38.2 | 9.4 | 47.7 | 14.9 | 75.6 | 1,800 | Natural |
| 25 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:41 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:41 AM | 255-HZS565-014 | 7.8 | 38.0 | 10.9 | 47.5 | 17.3 | 75.3 | 1,900 | Natural |
| 26 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:42 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:42 AM | 255-HZS565-020 | 11.0 | 38.7 | 14.5 | 48.4 | 23.1 | 76.8 | 2,800 | Natural |
| 27 | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:43 AM | Harshit | 15/07/2025 09:43 AM | 255-DZS565-006 | 3.5 | 19.1 | 4.7 | 23.8 | 7.5 | 37.8 | 1,800 | Natural |
| 28 | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:21 PM | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:21 PM | 360-CCCS565-014 | 7.5 | 709.5 | 10.8 | 882.9 | 15.0 | 1,385.4 | 100 | Natural |
| 29 | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:23 PM | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:23 PM | 360-CCCS565-200 | 120.0 | 722.4 | 169.4 | 900.2 | 262.8 | 1,411.7 | 1,600 | Natural |
| 30 | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:24 PM | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:24 PM | 360-CEZS565-028 | 17.0 | 745.6 | 21.8 | 927.9 | 34.3 | 1,456.1 | 220 | Natural |
| 31 | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:25 PM | Harshit | 17/07/2025 12:25 PM | 360-CEZS565-200` | 120.0 | 760.6 | 168.2 | 946.2 | 263.8 | 1,483.7 | 1,500 | Natural |
| Model No. | Continuous Rating Power (kW) | Continuous Rating Torque (Nm) | Power (kW) at 60 Minutes | Torque (Nm) at 60 Minutes | Power (kW) at 15 Minutes | Torque (Nm) at 15 Minutes | Rated Speed (RPM) |
Why Choose an Inverter Motor?
The growing adoption of inverter motors is driven by several key advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Since the motor speed is matched with load demand, unnecessary power consumption is eliminated. This often results in 20–50% energy savings compared to fixed-speed motors.
Extended Equipment Life: Smooth start/stop and reduced mechanical stress minimize wear on motors and connected machinery.
Precise Control: Inverter motors deliver accurate speed and torque regulation, which is essential in robotics, automation, and transport.
Flexibility: A single inverter motor can be configured for different voltage ranges, making it suitable for multiple industries and applications.
Types of Inverter Motors
Different motor technologies can be paired with variable-frequency drives. Each type has unique benefits depending on the application.
Induction Motors with VFDs
Traditional AC induction motors, when combined with a VFD, can run at variable speeds. They are widely used in pumps, fans, and conveyors where speed flexibility improves system efficiency.Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) with Inverters
PMSM motors use permanent magnets for excitation instead of field windings. When paired with inverters, they offer higher efficiency, compact size, and excellent torque control—ideal for electric vehicles and high-performance automation systems.Switched-Reluctance Motors (SRM) with Inverters
These motors generate torque by switching current across phases in sequence. When controlled by a VFD, SRMs provide precise speed regulation and high reliability under challenging conditions.AC Motors with Sensorless Vector Control
Advanced vector-controlled inverters allow AC motors to achieve near-servo performance without external feedback sensors. This reduces system cost while maintaining high levels of accuracy and torque.
Innotec Power – Permanent-Magnet Motor Manufacturer
At Innotec Power, we specialise in the design and manufacturing of permanent-magnet inverter motors for global OEMs. Our inverter motors integrate seamlessly with VFD controllers and can be tuned for either constant-speed operation or dynamic torque control, depending on customer requirements.
Key highlights of Innotec Power inverter motors:
Customizable Specifications: OEMs can define torque profiles, voltage ratings, and cooling methods.
Wide Voltage Range: Standard designs are available from 24V inverter motors to 350V inverter motors, while fully customised solutions can be engineered for specific needs.
High Efficiency: By using permanent magnets, our inverter motors achieve superior performance with lower energy losses.
Durability: Designed for heavy-duty and continuous applications, our motors are built to withstand industrial, automotive, and defence environments.
Choosing the Right Inverter Motor
When specifying an inverter motor for your application, several factors must be considered:
Application Requirements
Clearly define the purpose and duty cycle. For example, HVAC systems need inverter motors that operate efficiently at partial loads, while electric forklifts demand high-torque traction motors.Motor Specifications
Select the correct voltage (e.g., 72V inverter motor for auxiliary systems, 220V inverter motor for industrial use, or 350V inverter motor for hybrid vehicles). Match power and current ratings with your supply and desired performance.Operating Environment
Motors may require open drip-proof (ODP), totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC), or explosion-proof enclosures, depending on ambient conditions such as dust, humidity, or temperature.Control and Feedback
Decide if you require Hall sensors, resolvers, or sensorless control depending on the level of accuracy required for speed or position feedback.
Applications of Inverter Motors
Thanks to their adaptability and efficiency, inverter motors are deployed across a wide range of industries:
Electric Vehicles & Hybrids: High-power inverter motors drive the main propulsion, while 72V auxiliary inverter motors manage pumps, fans, and accessories.
Material Handling & Logistics: Conveyors, hoists, and AGVs (automated guided vehicles) use inverter motors for smooth acceleration and deceleration.
HVAC Systems: Fans, pumps, and compressors with VFD motors adjust speed dynamically, lowering energy bills in commercial buildings.
Industrial Automation: Robotics, CNC machines, and process equipment benefit from precise torque control.
Defence & Heavy Equipment: Rugged inverter motors operate reliably under extreme duty cycles and environmental conditions.

Partner with Innotec Power
Choosing the right inverter motor manufacturer is as critical as selecting the right motor type. At Innotec Power, we don’t just supply motors—we provide complete engineering support. Our services include:
Motor selection assistance based on your application.
Integration with variable-frequency drives to optimise performance.
Prototyping and testing to ensure the motor performs reliably in your real-world environment.
Custom design for specialised industries such as defence, off-highway equipment, and hybrid power systems.
By partnering with us, you gain a long-term collaborator who ensures your inverter motor system achieves maximum efficiency, durability, and performance.
